.NET with React vs Angular: Choose Your Front-End Framework

Introduction
Choosing the right front-end framework in 2025 isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a strategic business move. With Microsoft’s .NET ecosystem continuing to evolve, many development teams are integrating powerful front-end frameworks like React and Angular to deliver fast, scalable, and user-friendly web applications. Both React and Angular have matured into enterprise-ready technologies, but their differences are significant enough to influence how your application is built, scaled, and maintained.
In this guide, we will delve into the key differences between React vs Angular when used with the .NET stack, how each framework integrates with .NET Core, what type of applications they best support, and which option can provide better ROI, developer efficiency, and future-readiness in 2025.
Why Choosing the Right Front-End Framework Matters for .NET Applications
Your backend might be rock solid with .NET, but it’s the front-end experience that directly impacts how users engage with your application. In 2025, digital experiences are expected to be responsive, real-time, and seamless across all devices. Front-end frameworks like React and Angular play a pivotal role in delivering these expectations.
Moreover, the framework you choose can influence:
- Development speed and learning curve
- Scalability and maintainability
- Performance on different browsers/devices
- Developer community and resource availability
- Long-term technical debt and flexibility
A mismatch between the front-end and .NET backend could result in increased costs, performance bottlenecks, and a poor user experience.
Also Read – Unlocking the Power of .NET 9: Key Features Driving Faster, Scalable, and Smarter Applications
React with .NET – A Modular Powerhouse
React, originally developed by Facebook, is one of the most popular JavaScript libraries for building user interfaces. Its component-based architecture and declarative programming style make it an ideal choice for creating dynamic and high-performance UIs.
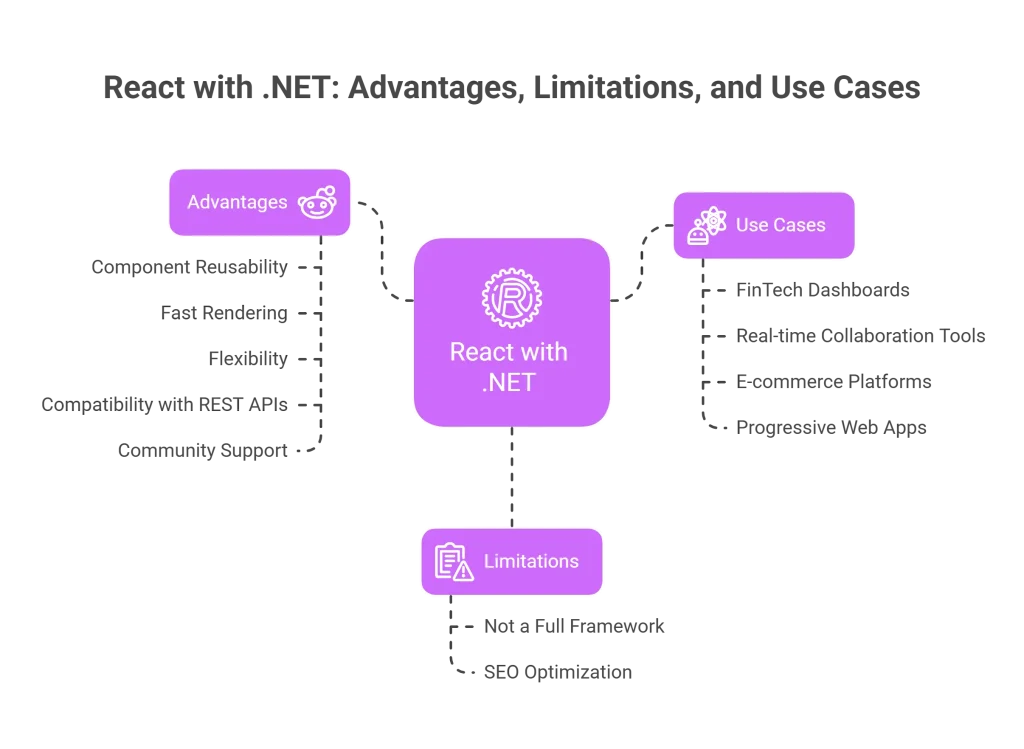
Advantages of Using React with .NET:
- Component Reusability: React modular structure lets you build self-contained components that are easy to test and reuse, which can drastically reduce development time and code duplication.
- Fast Rendering with Virtual DOM: React uses a virtual DOM to optimize rendering processes, which makes it faster and more responsive, especially useful for interactive and real-time applications.
- Flexibility and Ecosystem: React doesn’t enforce a specific project structure or pattern, giving developers the flexibility to choose tools like Redux, Zustand, or MobX for state management, and tools like Next.js for SSR.
- Strong Compatibility with REST APIs: React works seamlessly with .NET Core APIs, allowing you to create powerful frontend-backend integrations with minimal friction.
- Thriving Community & Support: With its vast ecosystem and resources, developers can find solutions, tutorials, and libraries for nearly any use case.
Limitations:
- React is not a full-fledged framework—it focuses only on the view layer. You’ll need to integrate other libraries for routing, form validation, and state management, which can complicate projects for teams unfamiliar with React ecosystem.
- SEO optimization requires additional tools like Next.js for server-side rendering, especially if you’re building public-facing applications.
React Works Best For:
- FinTech dashboards with high data interaction
- Real-time collaboration tools
- E-commerce platforms with dynamic user interactions
- Progressive Web Applications (PWAs) and mobile-first web apps
Angular with .NET – The Enterprise-Grade Framework
Angular is a full-fledged framework developed by Google and written in TypeScript, which Microsoft also supports. Its all-in-one architecture makes it an excellent choice for large-scale, structured applications that require long-term maintenance.
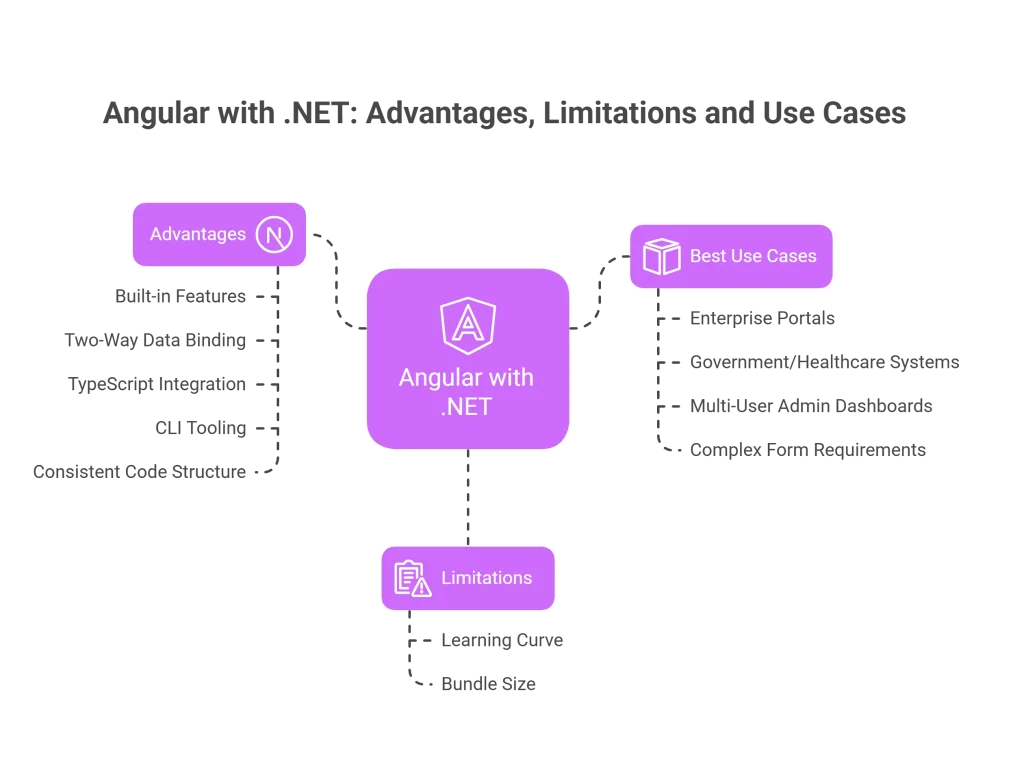
Advantages of Using Angular with .NET:
- Built-in Features: Angular includes routing, forms, dependency injection, HTTP client, testing tools, and more right out of the box, eliminating the need to install multiple libraries.
- Two-Way Data Binding: Angular has ability to synchronize the model and the view makes it easier to manage data changes without writing excessive boilerplate code.
- TypeScript Integration: Angular is built with TypeScript by default, which complements .NET’s C# language, making it easier for .NET developers to transition into Angular projects.
- CLI Tooling: In Angular Command Line Interface (CLI) offers powerful scaffolding tools, testing features, and production optimization commands that streamline the development lifecycle.
- Consistent Code Structure: Angular enforces architectural patterns and best practices that are beneficial in large teams and enterprise-level applications.
Limitations:
- Learning Angular can be challenging for teams not already familiar with its concepts like decorators, modules, and RxJS.
- Larger bundle sizes may affect performance in slow internet environments, although recent Angular updates have improved tree-shaking and lazy loading features.
Angular Works Best For:
- Enterprise portals like HRMS, CRM, or ERP
- Government or Healthcare systems with strict compliance needs
- Multi-user admin dashboards
- Applications with complex form and validation requirements
Side-by-Side Comparison: React vs Angular with .NET
| Feature | React with .NET | Angular with .NET |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Lightweight UI library | Complete front-end framework |
| Language | JavaScript or TypeScript | TypeScript only |
| Learning Curve | Easier to pick up | Requires deeper understanding |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and modular | Structured with set patterns |
| Tooling & CLI | Community-driven tools | Official Angular CLI with built-in features |
| Ecosystem | Decentralized, choose your own stack | Centralized, all-in-one solution |
| Performance | Fast for lightweight, dynamic apps | Optimized for large, complex apps |
| State Management | Custom via Redux, MobX, etc. | Built-in using RxJS |
| Best For | Real-time, interactive UIs | Enterprise-grade, large-scale applications |
2025 Trends and Framework Forecast
In 2025, React continues to dominate the startup and mid-sized project landscape due to its flexibility, ecosystem, and fast learning curve. On the other hand, Angular maintains its stronghold in large enterprises, especially in sectors like finance, healthcare, and government where structure, documentation, and standardization are key.
Newer advancements in both ecosystems—such as React Server Components, Angular Signals, and improved SSR/SSG tooling—are making both frameworks more powerful and efficient than ever before.
Additionally, .NET developers are increasingly embracing full-stack JavaScript front ends thanks to Microsoft’s ongoing support for JavaScript/TypeScript and REST-based APIs in ASP.NET Core.
Conclusion: What Should You Choose for Your .NET Application?
Your choice between React and Angular with .NET in 2025 should be informed by your project’s scale, complexity, team expertise, and business goals.
Pick React if you want maximum flexibility, a lightweight stack, and faster performance for dynamic user interfaces.
Choose Angular if you’re building enterprise-grade applications that require robust tooling, type safety, and long-term maintainability.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer—but with the right guidance, your decision can set your project up for long-term success.
Need help choosing the right front-end for your .NET application?
Partner with Codevision Technologies—our experts build scalable, high-performance solutions using React, Angular, and .NET tailored to your business goals. Let’s talk today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Absolutely. Pairing React with a .NET Core back-end is a very common and powerful combination. Your .NET application can serve data and logic through a web API, while React builds a fast and interactive user experience on the front-end. Development tools like Visual Studio even offer pre-built templates to get you started quickly.
This depends entirely on the needs of your project. Think of it this way:
- Angular is like an all-in-one toolkit. It’s a comprehensive framework that provides a clear, opinionated structure, which is ideal for large-scale enterprise applications where consistency and maintainability are key.
- React is more like a powerful, specialized engine that you build around. It offers more flexibility and is often preferred for projects that require a highly dynamic user interface or top-tier performance on specific components.
Both React and Angular remain premier choices for modern ASP.NET applications in 2025. The best fit comes down to your team’s goals. If you value a lightweight library and the flexibility to choose your own supplementary tools, React is an excellent option. If you need a fully integrated, out-of-the-box solution designed for complex enterprise scenarios, Angular is likely the more suitable path.
Yes, Microsoft fully embraces both frameworks. This support goes beyond simple approval; Microsoft provides official project templates, integration tools, and comprehensive documentation within Visual Studio and VS Code to ensure that connecting React or Angular to a .NET back-end is a smooth and well-supported process.
React often has the edge in initial page load speed and UI rendering, thanks to its use of a Virtual DOM, which minimizes direct manipulation of the webpage. However, for massive and complex applications, Angular has built-in optimizations like Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation can lead to better long-term performance and a more structured, manageable codebase.
It’s possible, but it is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning. Since this involves a complete rewrite of the front-end codebase, it’s not a simple switch. Teams often approach this gradually by migrating one feature at a time—a strategy known as a micro-frontend architecture—to minimize risk.
It often depends on your background. If you’re comfortable with TypeScript and object-oriented principles from working with C#, Angular structured approach may feel more natural. React, with its component-based architecture, might be quicker to pick up for UI-focused tasks, but keep in mind you’ll need to learn and integrate separate libraries for things like routing and state management, which Angular includes by default.
Both are highly effective for SEO, but they require an extra step called Server-Side Rendering (SSR). By default, these frameworks render on the client’s browser, which can make it harder for search engines to crawl your content. By implementing SSR (using tools like Next.js for React or Angular Universal), your .NET server can send a fully rendered, SEO-friendly HTML page to search engine crawlers, greatly improving visibility.
Definitely. Choosing either framework is a safe, forward-thinking investment for your projects. Both are backed by massive tech companies and global communities, and they are constantly evolving. React is pushing boundaries with features like Server Components, while Angular continues to focus on improving performance and the developer experience. Their integration with the .NET ecosystem is robust and set to remain a cornerstone of web development for the foreseeable future.

Modern Regulatory Reporting in Financial Services with Microsoft Power BI




